As organizations increasingly move into the cloud, remote work is now a necessity and common practice. Corporate boundaries have changed and become more fluid.
This means that maintaining networks and connections can be challenging given the limitations of some technologies. There has been a lot of controversy about the availability of the Zero-Trust Network (ZTNA), which replaces the traditional Virtual Private Networks (VPN). While ZTNA is certainly a viable solution for remote or cloud-based environments, VPN technology is not dead.
There are plenty of cloud citizen businesses. They will continue to work in the environment for the foreseeable future. VPN has many useful applications and will have many uses for years.
The first Internet Protocol Security Protocol (IPsec VPN), was created for a specific purpose: to connect people and websites to the internal network. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL VPN) is a different variant. This allows users to connect directly through their browser to the client site.
This narrow application of use cases means that there are inherent limitations in VPN design. It is specially designed to allow planning and implementation of policies before connecting, to control and limit access to each user and each network. This is done in conjunction with firewall rules and network fragmentation.
These limitations are the primary reason VPN technology is obsolete and at the end of its life. It is still a viable solution for many businesses. Many businesses are not fully committed to cloud computing and traditional solutions are in place, so VPN is still a viable option. Simply replacing this principle with a more efficient and effective one to obtain new technologies is expensive and confusing and ineffective.
The reason why ZTNA becomes important is when more cloud-based solutions are implemented, and the environment becomes less logical and therefore requires different controls. A zero-trust model provides access based on identity, regardless of the user’s location and can be granted according to the unique characteristics of the network the user is connected to. For example, if a user is connected to an established network, they may be given a higher level of access than connecting from an open network at an airport or coffee shop. This is not something you can do using a VPN.
ZTNA gives organizations the ability to manage access and set policies on a granular level, making it easier to troubleshoot and more compatible with a seamless network. ZTNA is not the last resort. It is a valuable and conceptual thing that must be part of a great architecture.
ZTNA is part of the Secure Access Service Edge system and is used with other components such as Secure Web Gateway, Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) and Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) to provide secure access to networks.
Take complicated matters seriously
As more companies connect to the cloud, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain a perimeter. This is why technology that can be used in an infinite space is important. ZTNA is the next step in wireless security, but it’s not a magic bullet. The best solution, or a combination of solutions, depends on a variety of factors, including the specifics of communication and environment, and the risk and budget of the company.
The VPN is not gone. It is a viable option, especially regarding the security of older systems. ZTNA becomes important when using cloud or Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions. However, as with all new technologies, a zero-reliance approach is expensive and can impact the business. To ensure that the business is using the best solution (and the most economical) for its needs it is important to work with a technical partner who understands the needs and the reliability of the system and can provide access without danger.
Simeon Tassev, MD and QSA at Galix
Follow IT Africa News on twitter
VPNs can’t magically encrypt your data – it’s not actually possible. You can’t change the fact that the endpoint expects a clear statement. The only encrypted VPN connection is the one you make to the VPN service provider.
Can SSL be used in site to site VPN?
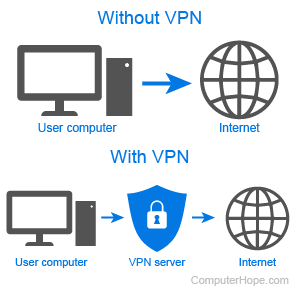
Site-to-site SSL VPN allows you to provide access between internal networks over the Internet using an encrypted tunnel. Tunnel endpoints act as a client or server. The client initiates the connection, and the server responds.
Can IPsec be used to establish a VPN-to-site? Site-to-site VPNs are permanent connections that can be used to secure communications between offices (ie sites). It is usually configured to establish an IPsec network connection between devices connected to the network.
Is SSL used in VPN?
An SSL tunnel VPN allows web browsers to securely access various network services that are not just web based through an SSL tunnel. These services may be proprietary networks or software that are designed for corporate use and cannot be accessed directly over the internet.
Is VPN the same as SSL?
SSL/TLS VPNs protect application traffic streams from remote users to an SSL/TLS Gateway. In other words, IPsec VPNs connect hosts or networks to a secure private network, while SSL/TLS VPNs connect user sessions securely to services in a closed network.
Is VPN based on IPsec or SSL?
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a VPN standard. It was introduced in the 1990s and is still in use. To access IPsec, third-party client software must be installed on the user’s computer. It cannot be accessed through a web browser.
What is required for site to site VPN?
To establish a site-to-site VPN between two sites using it requires a VPN gateway (router or firewall, VPN concentrator, or security device) such as Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) is required. on both pages.
What is a requirement of site-to-site VPN?
It requires a client/server model. It requires placing a VPN server on the side of the company’s network. It requires hosts to use VPN client software for secure traffic.
How do I create a site-to-site VPN?
To establish an Internet-to-Home VPN connection using a virtual gateway, follow these steps:
- Requirements.
- Step 1 Create a portal for customers.
- Step 2: Create a target portal.
- Step 3 Step 3: Configure the network.
- Step 4: Update your security group.
- Step 5: Set up a connection between the VPN server and the Site.
What is the difference between site to site VPN and SSL VPN?
A site-to-site VPN connects dispersed LANs through internet infrastructure. IPSec VPN or SSL VPN connects client devices to an internet-connected LAN through infrastructure.
What are the two types of site to site VPNs?
Virtual Private Network (VPN) are basically of two types:
- Remote VPN: Remote Access VPN allows users to connect to a private network and to access its resources and services remotely. …
- Web to Web VPN Also known as Router to Router VPN, Web to Web VPN is a type of VPN used by large companies.
What is site to site VPN?
A virtual private network (VPN) is a connection established between different networks. This can be a corporate network with several offices that work together or a branch network that has a main office and several branches.
What is SSL certificate for VPN?

An SSL certificate is an electronic certificate or data file that verifies the authenticity or the owner of a website. SSL is shorthand for Secure Sockets Layer. This protocol establishes an encrypted connection between your browser and the site you are browsing.
What is the SSL certificate used for? Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a standard security technique for establishing an encrypted connection between a server and a client, especially a web server (web page) and a browser, or a mail server and a mail client (for example, Outlook).
Do I need SSL certificate for VPN?
Your company’s data could be exposed to hackers if your employees don’t use secure SSL certificates with bits 2048. Make sure internal servers, Intranets, and Virtual Private Networks (VPN) are secured .
Is SSL certificate necessary?
Any SSL certificate is required for websites that require privacy. This is not all. Search engines keep tabs on websites they believe are unsafe. Sites without an SSL certificate will be http while those with encryption will show https in users’ browsers.
Does SSL VPN use certificates?
Secure SSL VPN based on digital certificates Most SSL VPN solutions use an independent certificate authority (CA), which controls communication access through digital certificates. Only the certificate provided by the product can be used to establish a connection to the VPN provider.
Does SSL VPN use certificates?
Secure SSL VPN based on digital certificates Most SSL VPN solutions use a certificate authority (CA) that controls network access using digital certificates. Only the certificate provided by the product can be used to establish a connection to the VPN provider.
Does VPN need SSL certificate?
SSL Certificates for Internet Servers (VPN). Internet servers or Private Networks (VPN), require greater security because personal and financial information is transmitted all over the world.
How is VPN different from SSL?
SSL/TLS VPNs secure application traffic from remote users to an SSL/TLS Gateway. IPsec VPNs connect hosts to a secure private network. SSL/TLS VPNs protect user sessions by providing services that are part of a secure network.
What is VPN in network security?
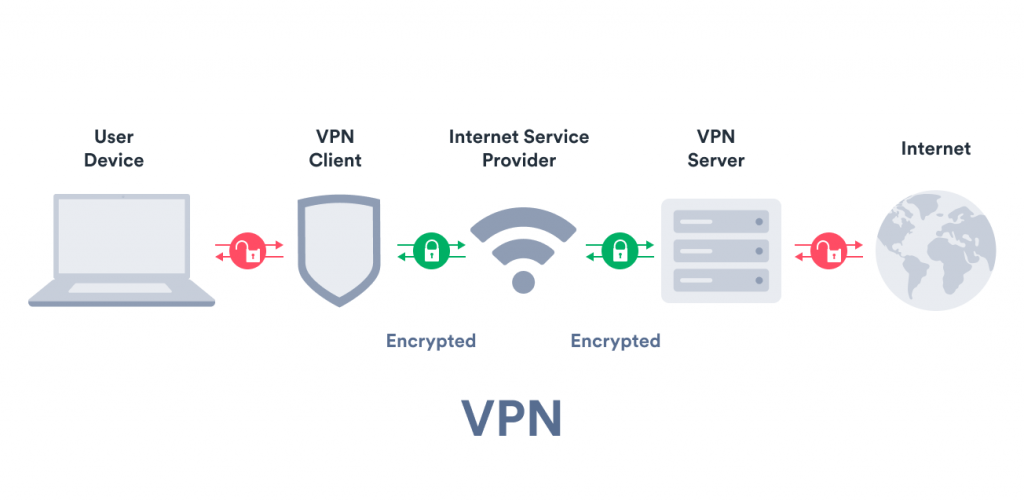
A VPN (private network) is an online service that creates an encrypted and secure connection. Internet users can use a VPN to give themselves more privacy and security online, or bypass region-based blocking or authentication.
What is a VPN and what are its types? Virtual Private Network (VPN) can be divided into two types: Remote VPN VPN and Remote Access VPN. A remote VPN allows users to connect to a private network and access its resources and services remotely. The Internet is used to establish a connection between a private network and a user. The connection is safe and secure.
What are 2 types of VPN?
Types of VPNs
- Site-to-Site VPN: A site-to-site VPN is designed to securely connect two distributed sites. …
- Remote VPN: Remote VPN is designed to connect remote users securely to a corporate network.
What are the two types of VPN connections choose two site to site?
Web-to-Web VPNs can come in one of two forms. Internet-based VPN: An intranet-based VPN connects two offices of the same business. It connects two separate LANs into one network. Extranet-based VPN: Some organizations need to connect to another organization’s network using an internet-based VPN.
What is the most common type of VPN?
11. Remote Access VPN Remote Access VPNs have become the most popular type of VPN. These VPNs connect users to remote servers located in a different country.
What VPN means?
What is a VPN and what is it? A VPN stands for “virtual private network” and is a service that allows you to stay private online. A VPN provides a secure, encrypted connection between your computer and the internet, providing an encrypted tunnel for your data and communications while you use public networks.
What is the main purpose of VPN?
The main function of a VPN is to hide your online activities. VPNs are used to protect against hackers and snoopers on public networks. However they hide your IP address, browsing history and personal data and other information on any Wi-Fi network, even at home.
What is the role of VPN in network security?
Your IP address is hidden from the Internet because the VPN server acts as a proxy (intermediary between your computer and the Internet). Malicious websites and other similar sites can only access your VPN server’s IP address, not your real IP address (a unique number that can identify any connected device).
What is the role of VPN?
VPN is short for private network. A VPN is an encrypted server that hides your IP address from governments, corporations and other hackers. A VPN protects your identity even when you use public or public Wi-Fi and your data is protected from any prying internet eyes.
What is VPN used for in enterprise?

VPNs can connect a user securely to a local network or the public Internet. VPNs are used by companies for remote workers to access company data and applications, or to create a shared network between multiple offices.
Why is a VPN important to a business help desk? A VPN helps you do your online activities through a secure tunnel, so hackers won’t have access to your valuable information.
What are two reasons a company would use a VPN?
- Secure Remote Access.
- Secure IoT Networks
- Secure Access to SaaS Applications
- Site-to-site Networking.
- Install Zero Trust.
- Web Threat Protection and Content Filtering
- Restricted Internet Access
What are two reasons a company would use a VPN select two?
What are the first two reasons a company would use a VPN? (Choose two.) Businesses use VPNs to provide a secure way to connect remote users, branch offices or suppliers to their network. A VPN gateway is essential for enabling VPNs.
What advantage does a VPN provide to enterprise business?
The purpose of a business VPN is to provide complete encryption for every device in your company’s network, which means that no snoops, hackers or even an internet service provider can view your location or information. This allows you to connect securely and privately to the Internet, regardless of the location of your computer.
What is a VPN and what is one advantage of using one in a business?
A VPN or Virtual Private Network is an encrypted connection between two machines. VPNs are ideal for remote work settings because employees can use VPNs to securely connect to their computers at work regardless of where they are.
How does a VPN impact a business?
You can reduce the chances of your company being targeted by using VPNs. VPN. VPNs boost productivity. If you have employees who are aware of the dangers of the internet they may be cautious about connecting to social networks.
What is the actual use of VPN?
VPN software protects your data by hiding your IP address, encrypting your data, and managing it through secure networks that connect servers in other states or countries. Doing so hides your online identity, ensuring that you can use the Internet safely and anonymously.
Do I really need a VPN at home?
A VPN is highly recommended in any case, especially working with sensitive data. It is important to turn it on at all times to protect yourself from data leaks, hackers and leaks, as well as snoopers, such as ISPs and advertisers. VPNs protect your privacy and protect your traffic from hackers and other cybercriminals.
Should VPN be on or off?
VPNs provide the best online security, and you should always leave your VPN running to protect yourself from cyber attacks and data leaks while using public Wi-Fi and against intruders. such as ISPs or advertisers. So always keep VPN enabled.
What is stronger than a VPN?

Tor is more effective than VPN VPN in the following cases: You want to be secure when accessing content that is geographically restricted. Tor is a great option to ensure your privacy when accessing content that is restricted in your country.
What is the difference between a proxy server and a VPN? Proxy servers and VPNs both mask your IP address. However, the difference is that a VPN can encrypt the data you send and receive, something a proxy server does not. A proxy server is not necessary if you already use a VPN.
Which of the VPN is the strongest?
NordVPN is a fast and secure VPN service that comes with unique features. It’s one of the most secure VPNs out there, combining AES-256 encryption with an ad and malware blocker, two VPN services, and multi-hop connectivity. NordVPN is the best choice if you want to hide your online presence.
What is the best type of VPN?
OpenVPN is the most popular protocol used by VPN professionals. It uses 256-bit encryption by default but also offers other encryption options such as 3DES (triple data encryption), Blowfish, CAST-128 and AES (Enhanced Encryption Standard).
Which VPN is best and fast?
Because of its lightning-fast speed and excellent performance, Surfshark is CNET’s current top pick for the fastest VPN. ExpressVPN comes in second place in our top VPN picks. It was awarded by CNET Editors as the best VPN overall. NordVPN is the third best option and is a big hit.
Is Tor safer than VPN?
While both Tor and VPNs work to protect online privacy, VPNs are the most secure option when used correctly. Tor is a free browser that encrypts your requests but it is not always fast and may not be able to access all sites. This can lead to legal problems.
Can I be tracked if I use Tor?
Tor Browser does not know your identity or location when you visit a website. Many websites ask for more information than they need through web forms. If you sign up to a website, they may not know where you are, but they know who you are.
Is Tor over VPN secure?
Yes! Connecting Tor with a VPN together will give you the best security.
Is there anything better than a VPN?
Two of the most popular options are software defined WAN (SD-WAN) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). SD-WAN is the most efficient alternative to VPN. Instead of using a point-to-point connection, SD-WAN provides a better way to manage encrypted data within the network of SD-WAN devices.
Is there a downside to having a VPN?
Like using a VPN service has some disadvantages. Performance, speed, and cost. Better encryption always brings potential lag. Using a VPN service can slow down your Internet connection because of the processing power required to perform encryption.
Is Tor better than a VPN?
A VPN protects your data and passes it through the server network. Tor, however, is a large network that is run by volunteers. It is less user-friendly and transparent, and slower and more complex. It’s still a powerful tool.
Sources :
