A VPN, or virtual private network, is a private network that spans a public network or the Internet. When traffic is connected to a VPN, the resulting flow of data is encrypted so third parties cannot intercept it. This makes it an ideal solution for online privacy and security.
A VPN can also be used to bypass geo-restrictions and censorship measures. They provide an extra layer of privacy and security for internet connections and are a great tool to increase online security and privacy.
See also: 7 challenges for enterprise networks
Although not native to any platform, third-party VPN client software makes it available on both iPhone and Android mobile phones. Using a VPN app might be less of a hassle to set up, but if it doesn’t give you the security, features, or performance you want, consider OpenVPN.
Why You Shouldn’t Use a VPN?
VPNs can’t magically encrypt your traffic – it’s just not technically possible. If the endpoint expects plaintext, there’s nothing you can do about it. When you use a VPN, the only encrypted part of the connection is from you to the VPN provider.
Why You Should Avoid Free VPN Using a free VPN is like a tunnel with countless holes that can expose your data or IP address. Hackers can track your activity, prying eyes can monitor you, and worse, you can be exposed to myriad privacy threats. Free VPN solutions are risky. They are a dangerous threat to your security and privacy.
Is it Safe to Use Free VPN?
Free VPNs are dangerous because they undermine your privacy instead of protecting it. In particular, some free VPN service providers do not have the resources to protect your data and prevent others from engaging in the unscrupulous practice of selling.
What are the disadvantages of a VPN?
What are the disadvantages of a VPN?
- With some VPNs, your connection may be slower.
- Certain websites block VPN users.
- VPNs are illegal or questionable in certain countries.
- There is no way of knowing how well a VPN encrypts your data.
- Some VPNs log and sell browsing data to third parties.
Do I need a VPN if I have antivirus?

You may think that having either an antivirus or a VPN is enough to ensure complete protection of your device and data. However, this is not the case as antivirus and VPNs offer slightly different protections. Both an antivirus and a VPN ensure protection from all possible angles.
Still need antivirus with a VPN? No, a VPN cannot effectively protect you from viruses. However, this does not protect your computer from malware most of the time, so you still need to use an antivirus program.
Do you offer NordVPN Antivirus?
Threat Protection is an antivirus feature launched by NordVPN in February 2022 that detects and blocks malware-infected files, websites, and spyware for safe browsing. It also improves CyberSec’s functioning, allowing it to stop intrusive ads and block trackers.
Does NordVPN protect your computer?
Your ISP cannot monitor what you do on the Internet or the websites you visit. Additional functions. Premium VPNs usually come with useful extra features. For example, NordVPN offers Threat Protection, a powerful cybersecurity tool that helps users avoid risky websites known for spreading malware.
What is the best example of VPN?
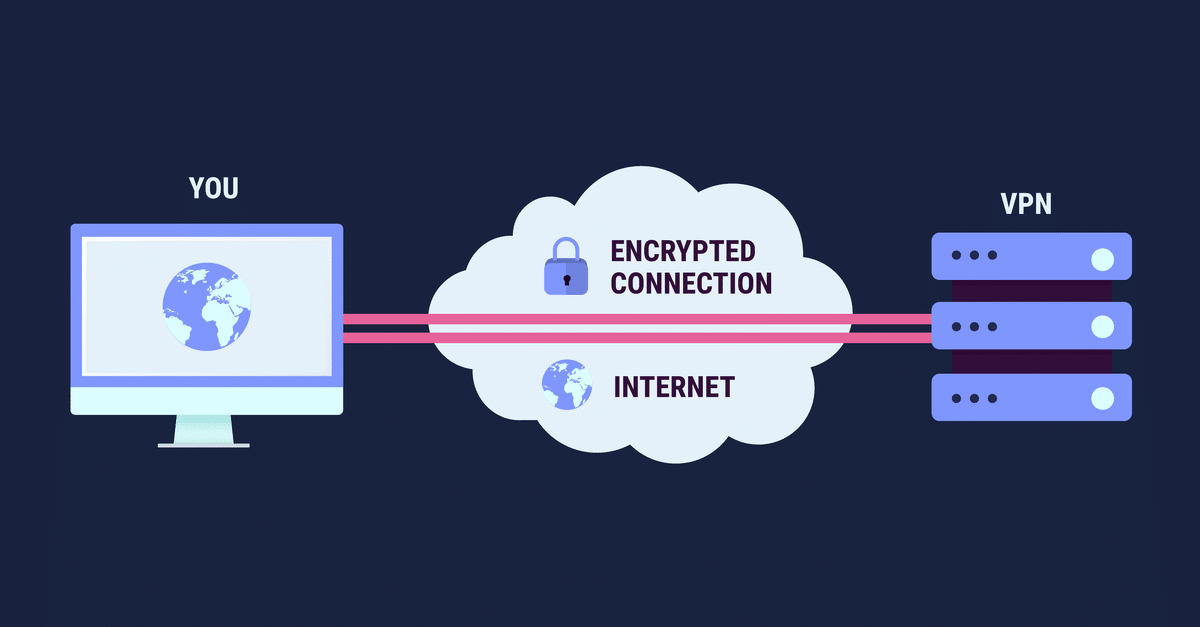
The best VPNs use encryption to protect our browsing data from being stolen by hackers, our ISPs or even the government….
- NordVPN.
- Surfshark.
- Private Internet Access VPN.
- IPVanish.
- ivacy
- Atlas VPN.
- ExpressVPN.
- PureVPN.
What is VPN an example of? Network-based VPNs are virtual private networks that securely connect two networks together over an untrusted network. A common example is an IPsec-based WAN, where all of a company’s offices are connected over the Internet using IPsec tunnels. There are different types of network VPNs.